From Sanxingdui to Shanxi Ancient Tombs: Innovative Applications of Hyperspectral Imaging in Cultural Relics Archaeology
三星堆遗址的考古发现持续为我们揭示古蜀文明的奥秘,而支撑这些发现背后的,是一项正在革新考古学研究方法的技术——高光谱成像。在最近的三星堆考古工作中,这项技术已成功应用于青铜器等珍贵文物的无损检测,帮助研究人员发现了许多被时间掩埋的历史细节。
高光谱成像技术通过采集数百个连续波段的光谱信息,实现文物"图谱合一"的精准检测,既能记录空间形态,又能分析物质组成,为考古研究提供多维数据支撑。本文以两个案例为切入点,阐述高光谱成像技术在文物考古领域的创新应用。
The archaeological discoveries at the Sanxingdui site continue to unveil the mysteries of the ancient Shu civilization, supported by a technology revolutionizing archaeological research methods—hyperspectral imaging. In recent Sanxingdui excavations, this technology has been successfully applied to non-destructive testing of precious artifacts such as bronze ware and ivory, helping researchers uncover historical details long buried by time.
Hyperspectral imaging captures spectral information across hundreds of continuous bands, enabling precise "image-spectrum integration" detection of cultural relics. It records spatial morphology while analyzing material composition, providing multidimensional data support for archaeological research. This article explores two case studies to illustrate the innovative applications of hyperspectral imaging in cultural relics archaeology.

三星堆文物,图片来源网络 / Sanxingdui artifacts, image source: internet
「三星堆:探寻古蜀文明的奥秘」
「Sanxingdui: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Ancient Shu Civilization」
三星堆遗址作为20世纪最伟大的考古发现之一,其出土的青铜器等文物具有高历史价值。然而,传统分析方法如X射线荧光分析、电子探针等存在明显局限:要么具有接触破坏性,要么只能反映局部特征。中科院西安光机所联合西北工业大学的研究团队将高光谱成像技术应用于这一领域,实现了文物保护与研究的双重突破。
As one of the greatest archaeological discoveries of the 20th century, the Sanxingdui site’s bronze ware, ivory, and other artifacts hold immense historical value. However, traditional analytical methods like X-ray fluorescence and electron microprobe have significant limitations—either being contact-destructive or only reflecting localized features. A research team from the Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics (Chinese Academy of Sciences) and Northwestern Polytechnical University applied hyperspectral imaging in this field, achieving breakthroughs in both cultural relic preservation and research.

遗址文物数据 / Archaeological site artifact data
该团队构建了一套完整的高光谱文物分析技术体系,在多个关键环节实现创新突破。
在数据采集与处理环节,开发了基于相对坐标的区域拼接算法,通过精确计算重叠区域面积和多尺度特征匹配,大幅提升了多轨图像拼接效率。该算法采用Dense SIFT算子进行快速特征提取,再通过RANSAC算法消除误匹配点,实现无缝拼接。
在特征提取方面,创新性地将空间注意力机制引入HRNet网络架构,通过特征图分解和ResNet结构聚合,显著提升了高分辨率图像的空间定位精度。同时构建了金字塔3D残差网络,采用渐进式特征维度增长策略,实现了对812个波段光谱特征的深度解析。
该技术在实际应用中展现出优秀的性能,已成功处理821帧不同分辨率的高光谱图像。通过对比实验,最终采用视觉映射模型的数据-决策级融合方案,使青铜器等目标的平均识别准确率达到0.84,ROC曲线分析显示AUC值较传统方法提升15%以上。
The team developed a comprehensive hyperspectral analysis system for cultural relics, making innovative advances in multiple key areas.
In data acquisition and processing, they created a region-stitching algorithm based on relative coordinates, significantly improving multi-track image stitching efficiency through precise overlap area calculation and multi-scale feature matching. The algorithm employs the Dense SIFT operator for rapid feature extraction, followed by the RANSAC algorithm to eliminate mismatched points, achieving seamless stitching.
For feature extraction, they innovatively integrated a spatial attention mechanism into the HRNet architecture, enhancing spatial localization accuracy in high-resolution images through feature map decomposition and ResNet-based aggregation. They also constructed a pyramid 3D residual network, adopting a progressive feature dimension growth strategy to enable in-depth analysis of spectral features across 812 bands.
This technology demonstrated exceptional performance in practical applications, successfully processing 821 frames of hyperspectral images at varying resolutions. Comparative experiments led to the adoption of a data-decision-level fusion scheme based on a visual mapping model, achieving an average recognition accuracy of 0.84 for targets like ivory and bronze ware. ROC curve analysis showed a 15%+ improvement in AUC values compared to traditional methods.

算法流程图 / Algorithm Flowchart
「山西古墓:解读地下的历史篇章」
「Shanxi Ancient Tombs: Deciphering Buried Historical Narratives」
山西南部某古墓底部存在大量黑色残留物,这些疑似古代文字或图案的痕迹因年代久远和环境侵蚀,肉眼已难以辨识。北京建筑大学与山西省考古研究所联合团队采用高光谱成像系统(波长范围400-1000nm,光谱分辨率0.6nm)对这一考古难题展开研究。
The bottom of an ancient tomb in southern Shanxi contained numerous black residues—faint traces suspected to be ancient writing or patterns, rendered nearly invisible to the naked eye due to age and environmental erosion. A joint team from Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture and the Shanxi Provincial Institute of Archaeology employed a hyperspectral imaging system (wavelength range: 400–1000 nm, spectral resolution: 0.6 nm) to study this archaeological challenge.
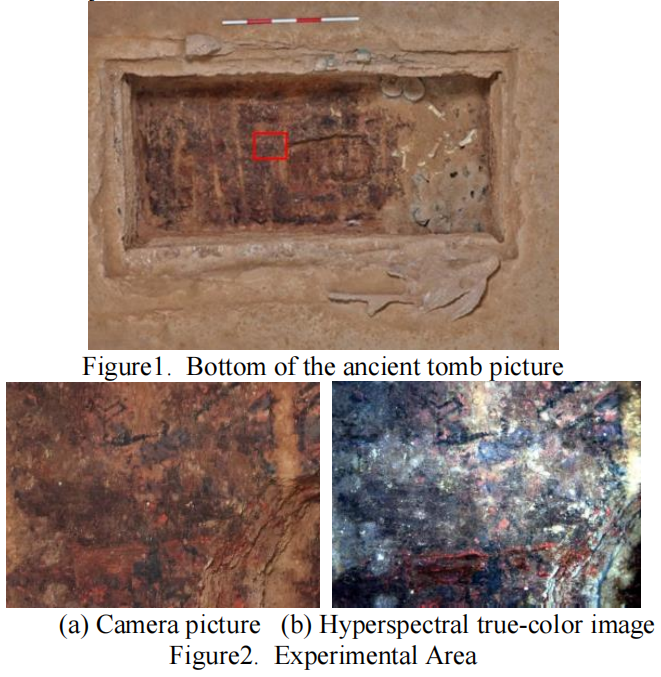
古墓底部的照片,及实验区域的高光谱图像 / Photos of the tomb floor and hyperspectral images of the experimental area
研究团队开发了完整的高光谱分析流程:首先通过辐射校正公式转换数据,有效消除了仪器噪声和光照干扰;然后筛选950个有效波段,利用主成分分析(PCA)浓缩信息;创新提出两个特征指数公式优化目标识别;最后运用多种形态学算法组合,生成15种处理方案,为考古人员提供了丰富的参考选择。
从考古价值来看,研究提供的多版本形态学处理结果成功重建了古墓底部疑似文字的连贯图案,这些图案在传统检测手段下无法辨识。这一发现不仅为解读该墓葬的文化内涵提供了全新实物证据,更展示了高光谱技术在非接触考古检测中的巨大潜力。
The team developed a complete hyperspectral analysis workflow: first converting data via radiometric correction formulas to eliminate instrument noise and lighting interference; then selecting 950 effective bands and condensing information using principal component analysis (PCA); innovatively proposing two feature index formulas to optimize target identification; and finally applying a combination of morphological algorithms to generate 15 processing schemes, providing archaeologists with rich reference options.
From an archaeological perspective, the multi-version morphological processing results successfully reconstructed coherent patterns of suspected writing on the tomb floor—patterns entirely undetectable using traditional methods. This discovery not only offers new physical evidence for interpreting the tomb’s cultural significance but also highlights the immense potential of hyperspectral technology in non-contact archaeological detection.

数据处理流程 / Data Processing Workflow
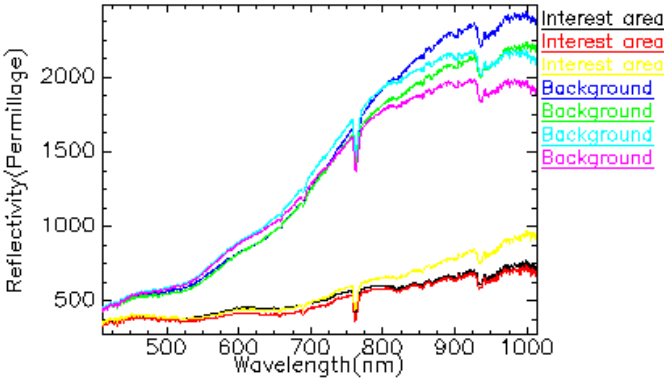
光谱曲线 / Spectral Curve
「结语 / Conclusion」
高光谱成像技术正在为文物考古提供了新的技术路径,帮助我们揭开历史尘封的面纱。这项技术不仅守护着文物安全,更让千年文明得以延续传承。
Hyperspectral imaging is forging a new technological path for cultural relics archaeology, helping lift the veil of history. This technology not only safeguards artifacts but also ensures the enduring legacy of millennia-old civilizations.
案例来源 / Source:
1. Qiu, S., Zhang, P., Tang, X., Zeng, Z., Zhang, M. et al. (2023). Sanxingdui Cultural Relics Recognition Algorithm Based on Hyperspectral Multi-Network Fusion. Computers, Materials & Continua, 77(3), 3783–3800.
2. Yang, X., Hou1, M., Lyu, S., Ma, S., Gao, Z., Bai, S., Gu, M., Liu, Y., & Hou, M. (2018). INFORMATION EXTRACTION IN TOMB PIT USING HYPERSPECTRAL DATA. ISPRS - International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2107-2111.
相关产品
免责声明
- 凡本网注明“来源:Ky开元集团”的所有作品,均为浙江兴旺宝明通网络有限公司-Ky开元集团合法拥有版权或有权使用的作品,未经本网授权不得转载、摘编或利用其它方式使用上述作品。已经本网授权使用作品的,应在授权范围内使用,并注明“来源:Ky开元集团”。违反上述声明者,本网将追究其相关法律责任。
- 本网转载并注明自其他来源(非Ky开元集团)的作品,目的在于传递更多信息,并不代表本网赞同其观点和对其真实性负责,不承担此类作品侵权行为的直接责任及连带责任。其他媒体、网站或个人从本网转载时,必须保留本网注明的作品第一来源,并自负版权等法律责任。
- 如涉及作品内容、版权等问题,请在作品发表之日起一周内与本网联系,否则视为放弃相关权利。
 手机版
手机版 Ky开元集团手机版
Ky开元集团手机版
 Ky开元集团小程序
Ky开元集团小程序
 官方微信
官方微信 公众号:chem17
公众号:chem17
 扫码关注视频号
扫码关注视频号



















 采购中心
采购中心